POW: Readers Needing More Support--Adapted Books with High Frequency Words
How do I get my readers more exposure to high-frequency or Red Words???
ADAPTED BOOKS
I love adapted books. My students LOVE them too! They are one of my favorite tools in my classroom. When it comes to building language skills or more experience with text--adapted books are a great way to effectively target specific skills in a way that is engaging for students.
What is an Adapted Book?
Adapted books are books that have been modified in some way and often make it easier for students with disabilities to use but I also find adapted books are more engaging for all students to read and target so many critical language skills. I create and use adapted books all the time because they are interactive, motivating, and target various language skills. Many allow the students to feel successful and part of the book because they have to add or move pieces within the book.
Why You Need Adapted Books?
Research tells us kids with severe and profound disabilities often get sub-par literacy instruction. Part of that is based on people’s assumptions about the abilities of students with complex disabilities, the idea that instructional materials should only focus on functional or sight word instruction, and fact that language skills are generally lacking for students in this population. The other part of that is a feeling that instructional materials are just not made for these students in a way that is accessible.
There are a couple of big targets you are trying to hit when you add adapted books or novels to your classroom and lessons. One of them is to increase a student’s access to literature. You would be amazed at how many classrooms have NO appropriate reading materials in their classrooms. Because our students take longer to learn new skills, available literature tends to be juvenile or fully functional.
It is imperative students with severe disabilities are exposed to developed ideas and advanced concepts as a means of improving overall literacy and adapted books are the perfect vehicle to do that.
Adapted books can vary in skill level and be used for a wide variety of students with different skill sets and literacy skills. Many times there are pictures associated with the vocabulary terms so it provides those extra visual supports to help with understanding and comprehension of the verbal message. As the books become more challenging students rely less on pictures and more on written words.
What is a High-Frequency Adapted Book?
Predictable texts are a specific type of book used in the earliest stages of reading instruction. It provides students with more frequent exposure to the targeted word. The texts have a repeated sentence or phrase on each page, typically with one variable word. A picture accompanies each sentence that allows the student to guess the variable word using the picture.
Errorless teaching is an instructional strategy that ensures children always respond correctly. Each page has only one answer--the target word. This means students are getting more frequent correct exposure to the word than reading authentic text where they can guess at the word.
Why Have Visuals Tied to Text?
Visuals are consistent. Visuals allow time for language processing. Visual prompts can offer a visual image and written word to meet the needs of a variety of students’ abilities. Visuals help students see what a word means. Visuals help to build independence.
So What Should I Do?
The first thing you should do is get this FREE adapted book by clicking here! Yeah. I love my readers… a lot. This is a very simple book.
Are you wanting more???? This bundle has 7 more to help you build your student's high-frequency reading knowledge.
Chat Soon-
PS--Bundle 2 coming soon
3 Fan Favoriate Phonemic Awareness Ideas (that are free)
What is Phonemic Awareness?
Phonemic Awareness (PA) is:
- the ability to hear and manipulate the sounds in spoken words and the understanding that spoken words and syllables are made up of sequences of speech sounds
- essential to learning to read in an alphabetic writing system, because letters represent sounds or phonemes. Without phonemic awareness, phonics makes little sense
- fundamental to mapping speech to print. If a child cannot hear that "man" and "moon" begin with the same sound or cannot blend the sounds /rrrrrruuuuuunnnnn/ into the word "run", he or she may have great difficulty connecting sounds with their written symbols or blending sounds to make a word
- essential to learning to read in an alphabetic writing system
- a strong predictor of children who experience early reading success
Why is it important?
- It requires readers to notice how letters represent sounds. It primes readers for print
- It gives readers a way to approach sounding out and reading new words
- It helps readers understand the alphabetic principle (that the letters in words are systematically represented by sounds)
...but difficult:
- Although there are 26 letters in the English language, there are approximately 40 phonemes, or sound units, in the English language
- Sounds are represented in 250 different spellings (e.g., /f/ as in ph, f, gh, ff)
- The sound units (phonemes) are not inherently obvious and must be taught. The sounds that make up words are "coarticulated;" that is, they are not distinctly separate from each other
What Does the Lack of Phonemic Awareness Look Like?
Children lacking phonemic awareness skills cannot:
- group words with similar and dissimilar sounds (mat, mug, sun)
- blend and split syllables (f oot)
- blend sounds into words (m_a_n)
- segment a word as a sequence of sounds (e.g., fish is made up of three phonemes, /f/ , /i/, /sh/)
- detect and manipulate sounds within words (change r in run to s)
Evidence Based Practices and the Big 5
Evidence-based practices in education are the same. They are backed by rigorous, high-standard research, replicated with positive outcomes, and backed by their effects on student outcomes. EBPs take the guesswork out of teaching by providing specific approaches and programs that improve student performance. There is frustration in teaching when you cannot find a way to help your student learn. You try one thing and then another and another and they are not having positive outcomes for your student. EBPs have proven outcomes on students’ performance and can make finding and implementing an effective practice less frustrating.
Using evidence-based practices (EBPs), with special education students especially, is a critical feature of improving their learning outcomes. When teachers combine their expertise as content knowledge experts with explicit instruction and practices and programs backed by research, the likelihood that a child will grow academically is increased.
A quick history lesson
We all love or hate the Big 5.
BUT..... without them
Congress appointed a National Reading Panel (NPR) in 1997 to review reading research and determine the most effective methods for teaching reading. The NRP reviewed over 100,000 studies and analyzed them to see what techniques actually worked in teaching children to read. The group only looked at quantitative studies, which gathered data in a numerical form and through structured techniques. Qualitative studies, which gather data through observations such as interviews were not included. In 2000 the NRP submitted their final report. The results became the basis of the federal literacy policy at that time, which included “No Child Left Behind.” We still base our understanding of evidence-based reading research on the NPR, but sadly, some of their major recommendations have been largely ignored. So what were their findings? They concluded that there were five essential components to reading, known as “The Big Five:”
- Explicit instruction in Phonemic Awareness.
- Systematic Phonics Instruction.
- Techniques to improve Fluency. These include guided oral reading practices where the student reads aloud and the teacher makes corrections when the student mispronounces a word. A teacher can also model fluent reading to the student. Fluency includes accuracy, speed, understanding, and prosody. Word calling is not the same as fluency.
- Teaching vocabulary words or Vocabulary Development.
- Reading Comprehension.
On top of this comes systematic Phonics. Children learn that the sounds in spoken words relate to the patterns of letters in written words. Not just mastery of the skills of systematic phonics, but automaticity in those skills, is also necessary for fluency to develop.
With these two layers in place and developed to the point of automaticity, techniques to improve Fluency can begin to be effective.
Vocabulary Development can be built next, including learning the meaning of new words through direct and indirect instruction, and developing tools like morphemic analysis, to discover the meaning of an unknown word.
Then Comprehension Skills can be added. Comprehension skills are the strategies a reader can use to better comprehend a text.
This is the foundation of reading, but it is also the foundation of education generally. Every subject is dependent on reading, and mastery of these subjects depends on developing a strong foundation in these early literacy skills.
As I continue to explore Evidenced-Based Practices, I will use the “Big 5” to share how they can be developed, and provide some resources that you can take back and use.
Chat Soon,
Evidence Based or Best Practice: The Beginning
Balanced literacy. Orton-Gilliamham. Think-Alouds. Graphic Organizers. Direct instruction. OMG!!!
Have you ever sat staring at your plans and IEPs and wonder how the #@& am I going to move this kid? Simply because of where the student sits in relation to their grade-level peers.
I have.
OR
I have so many with the same need but they didn’t make as much progress as I was hoping. (Or they needed to.)
Buildings don’t buy curriculum programs with special education students in mind. They might ask (if you're lucky) for your input. To be real, they buy with the larger in mind, which makes sense when you need to get the biggest bang for your buck.
What to do?????
In my building, moving students more than a year's growth is VERY important to us. We strive to close those gaps before they move to middle school.
I don’t have programs. Well, I have access to several but they can be (and most of the time) used by classroom teachers or worse the materials from the program were used but not the program itself.
I know I’m not the only one. So, what do you do???
OR
Want to learn what I do to get data that looks like this?

I had an Instructional Coach when I first started teaching, that showed me the value of putting time into learning and mastering both educational best practices and evidence-based practices. So even, if I was stuck with limited options, I could get tons of bang without a whole lot of stress.
Take guided reading, (yes, I know but you have to work with what you got), I became an expert at guided reading. I worked in tiny groups of two and three but with best practices and a couple of evidence-based practices, I was able to move kids to within months of their peers. (This brings up a whole different conversation when you can do this--is core really happening in the classroom or are they special education. I’m not going to answer those questions, as those are part of the larger school system.)
The Elementary Secondary Education Act defines evidence-based practices as those “effective educational strategies supported by evidence and research”. When teachers use evidence-based practices with fidelity, they can be confident their teaching is likely to support student learning.and
David Ardale defines best education practices as the wide range of individual activities, policies, and program approaches to achieving positive changes in student attitudes or academic behaviors.
Think Hattie and Marzano. (We all have a love/hate relationship with them)
Join me as I walk through how I use these ideas to get the most bang for your buck and move kids to close gaps with my special education students.
Send me your questions or if you're stuck and need help with. I’ll help you problem solve.
Chat soon,
Wait...Orton...What????
I came across Orton-Gillingham during a field placement as an undergrad. The special education teacher was using Wilson with her small groups to help them build reading skills. Mind you--this was not something taught in my program but she opened my eyes to something I would keep in my teaching bag.
The Orton-Gillingham approach is a multi-sensory way of teaching reading, spelling, and writing skills to students who struggle with language-based learning difficulties, including dyslexia. Lessons focus on mastery of the smallest units of language first, including phonemes and graphemes, and then build to whole word, phrase and sentence level instruction.
Important to note: Orton-Gillingham refers to an instructional approach, not any particular program or curriculum.
A Quick History Lesson
The term “dyslexia” first appeared in texts in the early 1870s. The Orton-Gillingham approach has been in use for the past 80 years and is the oldest dyslexia-specific approach to remedial reading instruction. It was developed in the 1930s by neuro-psychiatrist Dr. Samuel Orton based on his work with children who struggled with language processing issues but were of normal intelligence.
Dr. Orton proposed a neurological basis for the problem and developed a series of activities that combined right and left brain functions, predicting it would positively impact the ability to read and spell.
Dr. Anna Gillingham focused her efforts on training teachers in the approach, creating materials and expanding the instruction to include essential features of the English language, such as prefixes, suffixes, and even spelling rules.
Encouraged by Dr. Orton, she compiled and published instructional materials as early as the 1930s which provided the foundation for student instruction and teacher training. This collaboration became known as the Orton-Gillingham Approach.
What is Orton Gillingham?
This is where there seems to be a communication gap between parents and schools. OG is not a program, course or curriculum. There is no official “Orton Gillingham certification” for teachers. Your child does not get pulled out of their classroom an hour a day and taken someplace else to learn OG.
So what is OG then? First, it’s usually called the Orton Gillingham Approach.
And that’s what it is–an approach or way of teaching.
Orton-Gillingham places an important emphasis on multi-sensory approaches to learning. But it is more than that.
Orton-Gillingham is a highly structured approach, that breaks down reading and spelling into letters and sounds, and then building on these skills over time. OG was the first approach to use multi-sensory teaching strategies to teach reading.
This means that educators use sight, sound, touch, and motor movement to help students connect and learn the concepts being taught.
This multi-sensory approach helps students understand the relationship between letters, sounds, and words.
For example, an OG teacher a student to learn a letter by:
- seeing it
- saying it out loud
- sounding it out
- singing it
- writing it with pen or pencil
- writing it with fingers in shaving cream or sand
- forming it with clay or play-doh
- making the letter with your body or blocks
What is dyslexia?
Dyslexia is the most commonly diagnosed reading disorder. Dyslexia is also found on a continuum of severity, ranging from mild characteristics of dyslexia to profound difficulty with reading and writing. In its most severe forms, it is a learning disability. In its mildest form, it may be a source of puzzlement, frustration or mild inconvenience.
Dyslexia is a specific learning disability that is neurobiological in origin. It is characterized by difficulties with accurate and/or fluent word recognition and by poor spelling and decoding abilities.
As a result of this span of difficulty, the exact prevalence of dyslexia has yet to be definitively determined. It has been suggested that perhaps as many as 15% to 20% of the population as a whole have some of the symptoms of dyslexia (IDA, 2017).
Orton-Gillingham works because it enhances phonemic awareness in dyslexic individuals by examining common language patterns. Learners experiment with blending sounds, looking at letters and word parts in isolation and in various configurations, and studying language features, including diphthongs and silent letters.
The goal of Orton-Gillingham based instruction is to enable learners to decode words on their own and improve literacy skills in order to achieve their full potential at school.
Every state has its own special education legislation for the identification and special education support for students with a specific learning disability.
In Colorado, during the special education evaluation process, the team must document any characteristics of dyslexia. Be sure to look at your Department of Education--Special Education for what the team must do.
What the Orton-Gillingham Approach Can Teach Reading
The OG Approach can teach:
- Decoding: break words into their syllables and phonemes (the smallest unit of sound) to be able to read the word. Develops automaticity and fluency at the word level.
- Encoding: break down words orally into their syllables and phonemes to be able to spell the word.
However, an OG program requires supplemental programming to teach fluency and composition.
Can a Parent Teach Orton Gillingham?
Well, in the loosest form of OG, anyone can teach OG. All you need is a multi-sensory approach and you can say you’re OG. But just like too many behaviorists say they are using ABA (when they’re really not), OG is not for everyone either. This is where you have to be careful.
I’m not a BCBA, but I can reinforce ABA principles and activities at home with my son. I would say for most parents, you can reinforce tasks and lessons from school or at private tutoring. But unless you are a teacher or reading specialist, I would leave it to the experts.
Getting Orton Gillingham on your IEP
Want OG added to your IEP??? Ask the Team.
Ok, here’s where the troubles are, right? You asked for OG on your IEP, because it helps kids with dyslexia learn to read.
They said no. Ask for the progress monitoring data. So, what about trialing a change and getting back together in 30 days with data?
Have data??
Questions to ask:
- What is the data looking at? spelling (Encoding), reading (decoding)
- Is there improvement? How big?
- Ask the classroom teacher, what do they see?
- Ask the team, who is trained in which program? (Programs Accredited by IDA)
Fact is, many reading programs designed for students with dyslexia are based on the Orton Gillingham Approach. But the OG approach alone may not be enough to get them there.
Learning OG has been a wonderful and overwhelming journey but I have had students who are very successful with this approach and others who need a different approach to help them learn to read. It always comes back to the data.
Parents, always ask for it if the team doesn't bring it! Don't be afraid to push back on the team if they don't have it and ask questions about it and what it means for your child.
Chat soon,
101: MTSS & RTI
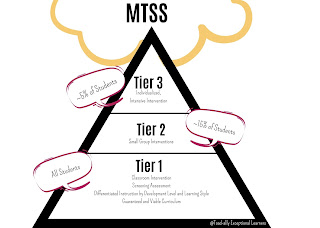
What is MTSS?
A Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS) is a framework of team-driven data-based problem solving for improving the outcomes of every student through family, school, and community partnering and a layered continuum of evidence-based practices applied at the classroom, school, district, region, and state level. MTSS is a coherent continuum of evidence-based, system-wide practices to support a rapid response to academic and behavioral needs, with frequent data-based monitoring for instructional decision-making to empower each student to achieve high standards.MTSS models rely on data to assess student needs and help teachers understand which kinds of intervention they need within each tier.
What is Response to Intervention?
Response to Intervention, or RTI, is an educational approach designed to help all learners to succeed, through a combination of high-quality instruction, early identification of struggling students, and responsive, targeted evidence-based interventions to address specific learning needs. RTI uses ongoing progress monitoring and data collection to facilitate data-based decision-making. In addition, the implementation of RTI will assist in the correct identification of learning or other disorders.
In my building, MTSS is the umbrella and RTI falls under it. All students are active participants in MTSS but not all students will be active participants in RTI.
How does RTI work?
It operates on a 3-tiered framework of interventions at increasing levels of intensity. The process begins with high-quality core instruction in the general education classroom. Teachers use a variety of instructional methods to maximize student engagement and learning: modeling of skills, small group instruction, guided practice, independent practice, to name a few.
Through universal screening methods, struggling learners are identified and are given more intense instruction and interventions that are more targeted to individual needs. By giving frequent assessments and analyzing data, teachers make decisions about what levels of intervention will best support student achievement.
What are the Tiers?
Tier I: This is the guaranteed and viable curriculum that all students receive each day within their general education classrooms. It is High quality, research-based core instruction in the general education classroom. All students are given universal screening assessments to ensure that they are progressing and are learning essential skills. {Sidenote: A guaranteed and viable curriculum is one that guarantees equal opportunity for learning for all students. Similarly, it guarantees adequate time for teachers to teach content and for students to learn it. A guaranteed and viable curriculum is one that guarantees that the curriculum being taught is the curriculum being assessed. It is viable when adequate time is ensured to teach all determined essential content.}
Within Tier 1, all students receive high-quality, scientifically based instruction provided by qualified personnel to ensure that their difficulties are not due to inadequate instruction. All students are screened on a periodic basis to establish an academic and behavioral baseline and to identify struggling learners who need additional support. Students identified as being “at-risk” through universal screenings and/or results on state- or district-wide tests receive supplemental instruction during the school day in the regular classroom. The length of time for this step can vary, but it generally should not exceed 8 weeks. During that time, student progress is closely monitored using a validated screening system and documentation method.
Tier II: More intensive, targeted instruction, matched to student needs, is delivered to students who are not making adequate progress in Tier I; they often receive instruction in small groups. They receive progress monitoring weekly, and teachers regularly evaluate data to assess whether students are making progress or need different or more intense intervention.
Targeted Interventions are a part of Tier 2 for students not making adequate progress in the regular classroom in Tier 1 are provided with increasingly intensive instruction matched to their needs on the basis of levels of performance and rates of progress. Intensity varies across group size, frequency and duration of intervention, and level of training of the professionals providing instruction or intervention. These services and interventions are provided in small-group settings in addition to instruction in the general curriculum. In the early grades (kindergarten through 3rd grade), interventions are usually in the areas of reading and math. A longer period of time may be required for this tier, but it should generally not exceed a grading period. Tier II interventions serve approximately 15% of the student population. Students who continue to show too little progress at this level of intervention are then considered for more intensive interventions as part of Tier 3.
Tier III: The most intensive, individualized level of intervention. Students who have not responded to Tier II intervention receive daily, small group or one-on-one instruction. Students in this level often are already receiving special education services, or are referred for further evaluation for special education.
Here students receive individualized, intensive interventions that target the students’ skill deficits. Students who do not achieve the desired level of progress in response to these targeted interventions are then referred for a comprehensive evaluation and considered for eligibility for special education services under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act of 2004 (IDEA 2004). The data collected during Tiers 1, 2, and 3 are included and used to make the eligibility decision. This is typically about 5% of your student population.
So what does all of this mean???
What that means is this. A teacher or parent identifies a student’s needs, and they try some interventions. Sounds simple enough, right?
So what’s the problem?
I have a family member who was struggling in reading. Mom talked to the teacher. The Teacher put the child in the RTI reading program. And she made progress and caught up with her peers.
That is the main benefit of RTI. For the right kid, with the right intervention, that’s all they need.
It can also look like a gifted student receiving enrichment in an area of strength like math.
The downside to RTI, it can feel like the school or district is stalling to identify special education needs. Remember, students are general education students first.RTI is a general education progress. It's open to all students who fall below a benchmark. In Colorado, we look at iReady cut scores. Interventions need to be evidenced-based (which doesn’t always happen). This means teachers have to progress monitor students to ensure they are making progress within the selected intervention and if they are not bring them to the building RTI team.
Every building works this process differently. In my building, we ask all teachers who have concerns about students to bring them to the RTI team. This ensures that teachers feel supported, the correct interventions are in place and should the student need to move forward with a special education evaluation the data the team needs is there. We also encourage parents to join the meetings. There is always a follow-up meeting scheduled 6 to 8 weeks out.
IDEA specifically addresses RTI and evaluations.
The 2004 reauthorization of IDEA makes mention of RTI as a method of part of the process of identifying SLD:
- In diagnosing learning disabilities, schools are no longer required to use the discrepancy model. The act states that “a local educational agency shall not be required to take into consideration whether a child has a severe discrepancy between achievement and intellectual ability[…]”
- Response to intervention is specifically mentioned in the regulations in conjunction with the identification of a specific learning disability. IDEA 2004 states, “a local educational agency may use a process that determines if the child responds to scientific, research-based intervention as a part of the evaluation procedures.”
- Early Intervening Services (EIS) are prominently mentioned in IDEA for the first time. These services are directed at interventions for students prior to referral in an attempt to avoid inappropriate classification, which proponents claim an RTI model does. IDEA now authorizes the use of up to 15% of IDEA allocated funds for EIS.
So this is the part where I expect to get pushback. But RTI has been overused and abused. Used to delay Special Education Evaluations and Services. Often.
So much so that the OSEP has put out multiple guidance letters about this.
If your child is in RTI and is doing well, great! I mean it! I am always happy to see a child’s needs being met. However, just have it on your radar that RTI is sometimes used to delay evaluations or IEPs. The old “Let’s try RTI and ‘wait and see.‘ ” Go with your gut. If you believe your child needs an IEP, request IEP evaluations.
Bonus tip: Your child can be going through the IEP evaluation process and receive RTI interventions at the same time!
Parents, how do you know if their children are making progress?
An essential element of RTI is ongoing communication between teachers and parents. As parents, you are kept involved and informed of the process every step of the way, beginning with notification that your child has been identified as struggling in one or more areas and will receive more intensive intervention. If your child receives more targeted instruction in Tier II or Tier III, he or she will be progress monitored frequently. Teachers will share progress monitoring data with you regularly through meetings, phone calls, or emails, as well as progress reports sent home showing assessment data.
When in doubt, ask the teacher for the data.
This is one way the process can look. The big piece for RTI to work is having the process monitoring data so decisions can be made timely.
Thinking Outside the Box with Math
Last time I mentioned spending more time looking at and using more “science” than “art” in my elementary resource room. Mostly, because I have no programming. That let me down what could have been a rabbit hole to find some sort of small group instruction but not sit and get. I mean even in my eight student math group, I have the same range you would find in a classroom and all at least two years behind.
Would it surprise you to know, that most special education resource rooms only do some version of sit and get? Differentiated but limit independent skills practice. Many times all these guys need is a reteach and time to practice—think guided release from Fisher and Frey. But what if you have kiddos who need more direction instruction—what do you do then? Bore one or move to fast for them to get the skill.
What this “idea” MUST have: guided direct instruction, varied independent practice, engagement, and easy to put together (both time and money).
Visible Learning research stresses:
- Focusing on progress: shifting from focusing on what teachers are doing to what students are learning
- Errors are welcome: creating a classroom where errors facilitate learning and growth
- Explicit success criteria: students know the learning intentions of each lesson and the criteria for success
- The right level of challenge: teachers set challenging goals, and offer students opportunities for deliberate practice to meet those challenges
Creating math centers has helped meet students' individual needs and continued to challenge everyone without the fear of failure and create an environment where risks are celebrated. I have found that thinking outside of the box is what has motivated students to do their best and reach for challenges and be more accepting with grappling with the material they don’t understand. But it didn’t come at the cost of having success criteria that pushes them to focus on their progress in math.
I’m not sure it means they changed their minds about math and they know like it but I do know they work harder during our math time. They ask more questions. They take more risks. But
- Direct Instruction
- Independent Skill Practice
- Technology
- Games
The Art and Science of Teaching
 |
Have to Teach Phonics? How???
What order should phonics be taught?
What about my students who struggle with reading? What can I do?

How I Increased Reading Fluency Scores
She is a second-grade student who has struggled with her self-confidence when reading and just learning how to read for the last year.
She represents the students I teach reading to every day.
- No self-confidence
- Beginning reader
- No strategies
- No sight word knowledge
Oh, but unlike others, they have increased their sight word knowledge by 50% in 15 weeks. They have self-confidence and strategies when approaching an unknown text. And classroom teachers, are seeing these changes when they are in guided reading.
How did I do this?
Most of the students I see during my day are beginning readers. Technically this means students reading Levels A-E. For students to read the book more than twice and NOT have the whole thing memorized, is a whole different problem. (If you have looked, just like I have, then you know it doesn’t exist.)
Passage Reading with Sight Words to the RESCUE
These passages pick up where guided reading leaves off. My students love the fact they can read 90% of the words so they can focus on their reading fluency.
Each passage starts with a one-minute cold read. Students graph their score.
When you come back the next day, I help them practice the passage as many times they want before timing it again.
Students keep the same passage until reaching mastery. [Chick here to get yours.]
REASONS WHY IT WORKS
It works because students are placed in reading passages at their independent reading level. This means they are not struggling with every word like they would in most reading fluency passages.
 I have written about Repeated Readings in the past as I create interventions--using John Hattie. My students love them and see each reading as a challenge to beat their score from the previous day. Tieing repeated reading with students doing their own data tracking has doubled their sight word scores and their grade level reading fluency scores.
I have written about Repeated Readings in the past as I create interventions--using John Hattie. My students love them and see each reading as a challenge to beat their score from the previous day. Tieing repeated reading with students doing their own data tracking has doubled their sight word scores and their grade level reading fluency scores.Student’s get tripped up on the sight words and can practice them without having to worry about the remaining text.
The Sight Word Cards are a way to quickly practice 5, 10, or 20 sight words. Each card is just for five days. [grab your here]
Max does his card as soon as he comes in. He started with reviews his personalized sight word deck of 10 cards and then moves right into his Sight Word Fluency Card.
He has struggled with learning his sight words since first grade. He never thought he would learn to read; let alone learn to love it!
I love that students graph their own data. This creates ownership and by-in. It builds self-confidence. It builds a love of reading.
I do all this fluency practice at the end of my lessons because it only takes 10 minutes. In those 10 minutes, I get daily progress monitoring of IEP goals, plan reading instruction, and build fluency.
By providing students with daily sight word fluency practice where students track their own data so that their instructional reading levels increase. Hattie's data adds evidence to what has become my go-to addition to their core intervention program.
In my district carry over back to grade level curriculum is HUGE! If it doesn't close gaps or classroom teacher don't see progress--you can forget about holding the course.
For those last ten minutes of group I spend focusing on reading fluency and sight words, I have seen a growth in sight words, self-confidence to attack more difficult text, and growth on grade level reading assessments.
My Classroom teachers are reporting student spending less time in their guided reading text because students are demonstrating solid decoding accuracy that has improved reading comprehension.
Chat Soon,

How I use WHY to Find Root Cause
Why?
How else are you going to figure out what the student’s needs really are!The Root Cause is so much more than just the test scores or the informal assessment scores you get. Getting to the bottom or root cause of why a student struggles takes a team, an open mind, and time. It's hard finding the one or two things that if you provide interventions or strategies for the student takes off.
My team most works on IEP goals. With the way building schedules have come together, it is all the time we have to work on. We work as a team to find the root cause behind their struggles. This is the process we use to find a student's Root Cause. When we work through a Root Cause Analysis we follow the same steps--make sure you bring an open mind and your data.
Scenario
Problem Statement: The student struggles with decoding.
Formal Reading Assessment
- Alphabet: 63%ile
- Meaning: 2nd%ile
- Reading Quotient: 16th%ile
Based on formal testing the student doesn’t have any decoding concerns but his Reading Comprehension score is significantly below the 12th%ile.
WHY?
I need more information.
DIBLES Scores for a 2nd grader
- Nonsense Word Fluency: 32 sounds; Benchmark 54 sounds in a minute; Gap 1.68
- Phoneme Segmentation Fluency: 47 sounds; Benchmark 40 sounds in a minute; Gap .85
- Oral Reading Fluency: 11 words; Benchmark 52 words in a minute; Gap 4.7
DIBELS shows the student knows their sounds and letters but there is something up with the oral reading fluency. There is a significant gap greater than 2.0.
WHY?
Complete:
- Error Analysis of ORF passage
- Assess sight words
- Does Phonological Processing need to be assessed?
Oral Reading Fluency error analysis shows 68% accuracy with 16 words read.
Assessing sight words show they know 41 of the first 100.
The decision was made based on what looks like a decoding weakness Phonological Processing was assessed--scores were in the average range.
What do I know now?
The student has a decoding weakness. He would benefit from a phonics highly structured phonics program.
Why??
This time I only needed three WHYS to figure out what the true problem is for the student. Sometimes you need more. On average it tends to run closer to five.
This process was completed with my team not during RTI. The decision to target phonics could have been reached without the formal testing and just with DIBELS and Sight Words.
My team uses this approach to help each other when we get stuck and need to take a step back and need more voices to look at the data.
As a special education team, we target only IEP goals and scaffold the student's skills up to access the grade-level curriculum. So the more specific we can be the better--we don’t want to waste time messing around with large messy goals that don’t end up helping the student close achievement gaps.
Go back to RTI.
How could this process be used during an RTI meeting?
Questions and dialogue are key concepts here. Talk about what the numbers tell you. Start with strengths and needs. Just the facts! Don’t interpret anything. Work through the data dialogue process as I outlined in the E-workbook: RTI Data Clarity freebie. I also included several worksheets to help teams work towards finding a student’s root cause.
Working to find the root cause of why a student is struggling is hard work. The dialogue with your team is a great way to bring in more voices. This in turns brings in more ideas that may help the student. Make sure you bring the Data Clarity e-workbook to help.
Do you similar to help your team find a student’s root cause? Feel free to brag about your success in the comments!
Are you wondering how you can use this idea with your team? Check out my free E-Workbook: RTI Data Clarity.
Chat soon,
Writing Best Practices
What are the best practices? Why??
As Resource Teacher, I don’t spend any time teaching in the Writers Workshop. I tend to focus on the science of writing. Can the student write in complete sentences? Does it make sense? Spelling? Handwriting? What accommodations does the student need to do Workshop in class?
Over the last couple of weeks, I have had parents ask me about writing. I have never really thought about the best practices in writing and how to guide teachers to build them into their writing practices.
The effective teaching of writing involves all three of these learning experiences, with an emphasis on the writer’s craft, the use of high-quality writing exemplars, time for classroom writing practice and thoughtful reflection before, during, and after the writing.
Best practices in Writing
1.Establish a positive atmosphere for writing, reading, and learning by:- Creating an inviting classroom with flexible seating, accessible resources, and attractive surroundings
- Modeling respect
- Sharing the teacher’s own writing with students
- Establishing routines and expectations
- Setting up a writing workshop routine which convenes every day of the week
- Using writer’s notebooks/portfolios
- Teaching writer’s craft techniques based on an understanding of the writing process and student writing needs
- Promoting student choice and ownership for both fiction and nonfiction writing
- Providing opportunities for authentic writing
- Giving reading an integral role in the writing classroom
- Providing diverse reading materials modeling the importance of craft and idea
5. Write regularly across the curriculum and grade levels by:
- Collaborating on assignments among content area teachers
- Sharing writing rubrics across grade levels and subject areas
6.Arrange for students to have a constructive response to their writing and to offer a response to other writers by:
- Making teacher and peer response a part of writing instruction
- Providing class time for revision
- Responding intermittently throughout the writing process, not only after the final draft
- Using many techniques to respond to student’s writing
- Using collaboration techniques such as furniture placement, modeling collaboration, providing checklists and forms, and organizing writing pairs or small groups
- Providing guidelines and demonstrations of appropriate student interactions and creating specific tasks for students to accomplish during their collaborations
- Choosing writer’s craft lessons that relate to students’ needs
- Structuring mini-lessons so students can observe, discuss, and simulate the targeted writing craft lessons or skills
- Providing specific responses to these simulated practices
How do I all of this in Workshop Model?
1.WRITING ALOUD- Teacher demonstrates
- Teacher models aloud what they are doing, thinking and rethinking while writing, rereading and revising a draft
- Teacher talks aloud about topics such as appropriate writing mode - narrative, expository, persuasive; spacing needs; organizational patterns and transition words; writer’s craft lessons such as persuasive details of statistics and expert opinion; effective repetition
- Teacher points out skills such as spelling conventions, punctuation needs, vocabulary choices, sentence structures, revision techniques
- Teacher and class compose aloud, collaboratively
- Both negotiate topics, purposes, and word choice with each other
- Teacher acts as scribe and encourages all students to participate
- Teacher provides explicit questioning and directions, encouraging high-level thinking on focus, support, organization, language use/ conventions, writer’s craft
- Core of the program – whole class, small group, or individualized
- Student writes and teacher guides
- Explicit teaching in form of mini-lessons for reinforcement of skills depicted in shared writing or for the introduction of new writer’s craft lessons
- Rubric development and review conferences take place along with peer response and sharing
- Writing may be responses to literature; authentic responses; relating to information/ reports; description of classroom experiences; personal reflections; writing to learn in content areas
- Writing activities are embedded each day
- Students work alone, using their current knowledge of writing process, often choosing own topics
- Occurs daily in writer’s workshop format
- Teacher and student monitor through daily log journals, conferences, teacher feedback
Balanced Writing Workshop?
How do these four components look in the classroom?- Reading-writing connection - tying together books being read aloud and/or studied in class to writing lessons and research reports/projects
- Meaningful print-rich environment – using labels, posters, captions where they catch student’s attention and serve a purpose for writing; literacy centers at K-5 such as post office, supermarket, bookstore, office, kitchen; real-world assignments
- Teacher modeling – regularly modeling aloud the drafting of narratives, leads, poetry, punctuation conventions, along with writing in response to reading assignments
- Real purposes and audiences – providing students time to write each day about topics they have knowledge of and care about, using rubrics which describe levels of achievement
- Writer’s craft – specifically teaching the techniques of writing such as the importance of audience, the use of dialogue, connotative and sensory language, parallel sentence structures
- Writing various genres – producing picture books, recipes, brochures, essays, social studies reports, movie reviews, website reviews, letters to the editor, book reviews, memoirs
- Emphasis on revision – revising pieces thoughtfully over time—not a new piece of writing each day
- Conferencing– keeping a log or portfolio on each student’s writing progress
- Spelling and vocabulary – connecting both to writing, reading and language use (Spelling should be part of writing)
- Sentence structure and conventions – practicing in context, using mini-lessons, not isolated skills sheets.
Caveats Regarding Two Teaching Practices
Teaching just the science of writing is the first area of concern. Too often, the science writing leads to mediocre, dull writing where student engagement with the text is absent.It is not that most students who just use a form cannot write; it is that they cannot write at the level that today’s businesses and colleges expect. Writing which is purposeful reflects insight into the writing situation and demonstrates a mature command of language.
While a formula may be useful for beginning writers who need scaffolding in organizational techniques and in the crafting of elaboration, it should not be an outcome expectation for student writers at any grade level.
Students need the art of writing to encourage student engagement with the text. This learning and practicing an array of organizational writing patterns also encourages higher order thinking. Teachers who teach a menu of organizational patterns, along with each pattern’s linking expressions and signal words, implicitly help students make sense of the ideas they want to express. Among these patterns are chronological order, comparison-contrast, description, concept/definition, and process/ cause-effect. Creative, thoughtful modes of writing may be developed through the use of these patterns– modes such as the personal essay, research report, autobiography, feature news article or editorial, as well as, the short story or poem.
Providing models of the art and craft of writing by excellent writers for student imitation is considered a best practice.
Like all Best Practices--it's about knowing your students and what they need to do their best work. With writing, the challenge is balancing the art and science of writing is required to create powerful, college ready writers.
Chat soon,

About Me
Resource Library
Thank you! You have successfully subscribed to our newsletter.