101: MTSS & RTI
What is MTSS?
A Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS) is a framework of team-driven data-based problem solving for improving the outcomes of every student through family, school, and community partnering and a layered continuum of evidence-based practices applied at the classroom, school, district, region, and state level. MTSS is a coherent continuum of evidence-based, system-wide practices to support a rapid response to academic and behavioral needs, with frequent data-based monitoring for instructional decision-making to empower each student to achieve high standards.MTSS models rely on data to assess student needs and help teachers understand which kinds of intervention they need within each tier.
What is Response to Intervention?
Response to Intervention, or RTI, is an educational approach designed to help all learners to succeed, through a combination of high-quality instruction, early identification of struggling students, and responsive, targeted evidence-based interventions to address specific learning needs. RTI uses ongoing progress monitoring and data collection to facilitate data-based decision-making. In addition, the implementation of RTI will assist in the correct identification of learning or other disorders.
In my building, MTSS is the umbrella and RTI falls under it. All students are active participants in MTSS but not all students will be active participants in RTI.
How does RTI work?
It operates on a 3-tiered framework of interventions at increasing levels of intensity. The process begins with high-quality core instruction in the general education classroom. Teachers use a variety of instructional methods to maximize student engagement and learning: modeling of skills, small group instruction, guided practice, independent practice, to name a few.
Through universal screening methods, struggling learners are identified and are given more intense instruction and interventions that are more targeted to individual needs. By giving frequent assessments and analyzing data, teachers make decisions about what levels of intervention will best support student achievement.
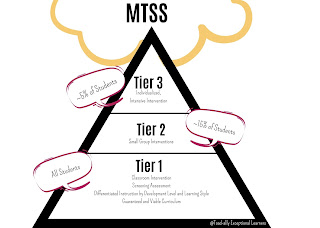
What are the Tiers?
Tier I: This is the guaranteed and viable curriculum that all students receive each day within their general education classrooms. It is High quality, research-based core instruction in the general education classroom. All students are given universal screening assessments to ensure that they are progressing and are learning essential skills. {Sidenote: A guaranteed and viable curriculum is one that guarantees equal opportunity for learning for all students. Similarly, it guarantees adequate time for teachers to teach content and for students to learn it. A guaranteed and viable curriculum is one that guarantees that the curriculum being taught is the curriculum being assessed. It is viable when adequate time is ensured to teach all determined essential content.}
Within Tier 1, all students receive high-quality, scientifically based instruction provided by qualified personnel to ensure that their difficulties are not due to inadequate instruction. All students are screened on a periodic basis to establish an academic and behavioral baseline and to identify struggling learners who need additional support. Students identified as being “at-risk” through universal screenings and/or results on state- or district-wide tests receive supplemental instruction during the school day in the regular classroom. The length of time for this step can vary, but it generally should not exceed 8 weeks. During that time, student progress is closely monitored using a validated screening system and documentation method.
Tier II: More intensive, targeted instruction, matched to student needs, is delivered to students who are not making adequate progress in Tier I; they often receive instruction in small groups. They receive progress monitoring weekly, and teachers regularly evaluate data to assess whether students are making progress or need different or more intense intervention.
Targeted Interventions are a part of Tier 2 for students not making adequate progress in the regular classroom in Tier 1 are provided with increasingly intensive instruction matched to their needs on the basis of levels of performance and rates of progress. Intensity varies across group size, frequency and duration of intervention, and level of training of the professionals providing instruction or intervention. These services and interventions are provided in small-group settings in addition to instruction in the general curriculum. In the early grades (kindergarten through 3rd grade), interventions are usually in the areas of reading and math. A longer period of time may be required for this tier, but it should generally not exceed a grading period. Tier II interventions serve approximately 15% of the student population. Students who continue to show too little progress at this level of intervention are then considered for more intensive interventions as part of Tier 3.
Tier III: The most intensive, individualized level of intervention. Students who have not responded to Tier II intervention receive daily, small group or one-on-one instruction. Students in this level often are already receiving special education services, or are referred for further evaluation for special education.
Here students receive individualized, intensive interventions that target the students’ skill deficits. Students who do not achieve the desired level of progress in response to these targeted interventions are then referred for a comprehensive evaluation and considered for eligibility for special education services under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act of 2004 (IDEA 2004). The data collected during Tiers 1, 2, and 3 are included and used to make the eligibility decision. This is typically about 5% of your student population.
So what does all of this mean???
What that means is this. A teacher or parent identifies a student’s needs, and they try some interventions. Sounds simple enough, right?
So what’s the problem?
I have a family member who was struggling in reading. Mom talked to the teacher. The Teacher put the child in the RTI reading program. And she made progress and caught up with her peers.
That is the main benefit of RTI. For the right kid, with the right intervention, that’s all they need.
It can also look like a gifted student receiving enrichment in an area of strength like math.
The downside to RTI, it can feel like the school or district is stalling to identify special education needs. Remember, students are general education students first.RTI is a general education progress. It's open to all students who fall below a benchmark. In Colorado, we look at iReady cut scores. Interventions need to be evidenced-based (which doesn’t always happen). This means teachers have to progress monitor students to ensure they are making progress within the selected intervention and if they are not bring them to the building RTI team.
Every building works this process differently. In my building, we ask all teachers who have concerns about students to bring them to the RTI team. This ensures that teachers feel supported, the correct interventions are in place and should the student need to move forward with a special education evaluation the data the team needs is there. We also encourage parents to join the meetings. There is always a follow-up meeting scheduled 6 to 8 weeks out.
IDEA specifically addresses RTI and evaluations.
The 2004 reauthorization of IDEA makes mention of RTI as a method of part of the process of identifying SLD:
- In diagnosing learning disabilities, schools are no longer required to use the discrepancy model. The act states that “a local educational agency shall not be required to take into consideration whether a child has a severe discrepancy between achievement and intellectual ability[…]”
- Response to intervention is specifically mentioned in the regulations in conjunction with the identification of a specific learning disability. IDEA 2004 states, “a local educational agency may use a process that determines if the child responds to scientific, research-based intervention as a part of the evaluation procedures.”
- Early Intervening Services (EIS) are prominently mentioned in IDEA for the first time. These services are directed at interventions for students prior to referral in an attempt to avoid inappropriate classification, which proponents claim an RTI model does. IDEA now authorizes the use of up to 15% of IDEA allocated funds for EIS.
So this is the part where I expect to get pushback. But RTI has been overused and abused. Used to delay Special Education Evaluations and Services. Often.
So much so that the OSEP has put out multiple guidance letters about this.
If your child is in RTI and is doing well, great! I mean it! I am always happy to see a child’s needs being met. However, just have it on your radar that RTI is sometimes used to delay evaluations or IEPs. The old “Let’s try RTI and ‘wait and see.‘ ” Go with your gut. If you believe your child needs an IEP, request IEP evaluations.
Bonus tip: Your child can be going through the IEP evaluation process and receive RTI interventions at the same time!
Parents, how do you know if their children are making progress?
An essential element of RTI is ongoing communication between teachers and parents. As parents, you are kept involved and informed of the process every step of the way, beginning with notification that your child has been identified as struggling in one or more areas and will receive more intensive intervention. If your child receives more targeted instruction in Tier II or Tier III, he or she will be progress monitored frequently. Teachers will share progress monitoring data with you regularly through meetings, phone calls, or emails, as well as progress reports sent home showing assessment data.
When in doubt, ask the teacher for the data.
This is one way the process can look. The big piece for RTI to work is having the process monitoring data so decisions can be made timely.

About Me
Resource Library
Thank you! You have successfully subscribed to our newsletter.


















0 comments:
Post a Comment